

Are you a special individual with the Rh-negative blood?
If the answer is Yes, you’re body’s immune system is unique, having the ability to produce antibody to the red cells that have the Rho (D) antigen. This antibody, called Anti-D, resides in the plasma, and is an essential component used in the manufacture of Rh immune globulin.
During pregnancy and childbirth, the Rh(D) factor plays an important role. All expectant mothers who are Rh-negative are advised to undergo preventative treatment and receive Rh immune globulin during and after pregnancy to prevent the baby to may develop brain damage, jaundice, or even die.
...Read moreProblem
Every person is unique, and so are the characteristics of your blood. Because everyone belongs to one of four blood groups: A, B, AB, or O. In addition, every individual inherits a set of Rh genes from each parent.
If a person has at least one D gene, they are considered Rh-positive. If no D gene is present, then that individual is considered Rh-negative.
This Rh factor may seem like a small thing, but it can lead to big complications. Let’s say, for example, that a mom-to-be has Rh-negative blood, but her baby’s blood is Rh-positive. During pregnancy, certain situations like prenatal examination, chorion biopsy, amniocentesis, obstetric interventions, miscarriage, or during childbirth itself, can cause the red blood cells of the fetus to pass into the bloodstream of the mother. This causes the baby’s Rh-positive blood to be registered by the immune system of the mother as a foreign protein. The woman now has been “inoculated” against Rh-positive blood. This is called Rh sensitization, and the mother’s defense system has learned to form antibodies for Rh-positive blood. This sensitization will not generally affect her initial pregnancy, but can have consequences for her future pregnancies.
If a mother has gained Rh sensitization from an earlier pregnancy and then becomes pregnant again with a Rh-positive child, her antibodies may in some instances cross the placenta barrier and attack the red blood cells of the unborn child, causing complications such as jaundice, brain damage, and in rare cases, death. Thanks to Rh immune globulin, Rh sensitization formation during pregnancy can be avoided in most cases.
All expectant mothers who are Rh-negative are advised to undergo preventative treatment and receive Rh immune globulin during and after pregnancy to avoid any of these complications. Unfortunately, the raw material source for production of Rh immune globulin has now become scarce. If the Anti-D plasma supply continues to decline, we fear one day the immunization of Rh immune globulin would not be available for the expectant mothers in need.
Every person is unique, and so are the characteristics of your blood. Because everyone belongs to one of four blood groups: A, B, AB, or O. In addition, every individual inherits a set of Rh genes from each parent.
If a person has at least one D gene, they are considered Rh-positive. If no D gene is present, then that individual is considered Rh-negative.
This Rh factor may seem like a small thing, but it can lead to big complications. Let’s say, for example, that a mom-to-be has Rh-negative blood, but her baby’s blood is Rh-positive. During pregnancy, certain situations like prenatal examination, chorion biopsy, amniocentesis, obstetric interventions, miscarriage, or during childbirth itself, can cause the red blood cells of the fetus to pass into the bloodstream of the mother. This causes the baby’s Rh-positive blood to be registered by the immune system of the mother as a foreign protein. The woman now has been “inoculated” against Rh-positive blood. This is called Rh sensitization, and the mother’s defense system has learned to form antibodies for Rh-positive blood. This sensitization will not generally affect her initial pregnancy, but can have consequences for her future pregnancies.
If a mother has gained Rh sensitization from an earlier pregnancy and then becomes pregnant again with a Rh-positive child, her antibodies may in some instances cross the placenta barrier and attack the red blood cells of the unborn child, causing complications such as jaundice, brain damage, and in rare cases, death. Thanks to Rh immune globulin, Rh sensitization formation during pregnancy can be avoided in most cases.
All expectant mothers who are Rh-negative are advised to undergo preventative treatment and receive Rh immune globulin during and after pregnancy to avoid any of these complications. Unfortunately, the raw material source for production of Rh immune globulin has now become scarce. If the Anti-D plasma supply continues to decline, we fear one day the immunization of Rh immune globulin would not be available for the expectant mothers in need.


The Life-Saving
Solution-You!
To prevent this shortage, Rh-negative individuals, like you, are immunized to produce antibodies in their blood. The immunization elicits an immune response with the production of the D antibody. When the antibody reaches a certain strength, your plasma is collected for the manufacture of Rh immune globulin. It is possible you are someone who already has developed the antibody from a transfusion or past pregnancy. You too would be given small amounts of Rhpositive red cells to strengthen the antibody. Once the plasma reaches the appropriate strength, your plasma would then be collected for the manufacture of Rh immune globulin.
...Read moreDonor Facts
Yes, the requirements are as follows:
- Able to meet the requirements of being a source plasma donor
- If female, post-menopausal or surgically sterile
- Willing to make a commitment to the program and plan to remain in the geographic area to make the lengthy process worthwhile
- Not donating whole blood or plasma at any other facility while in the program
Women of childbearing age must provide documentation from a physician or have a medical record that states surgical sterility or post-menopausal state (in other words, without the ability to conceive and have children). Women past child-bearing age do not need any documentation.
The steps are simple:
- Undergo a screening medical evaluation by our physician to determine your eligibility for this program. This is at no cost to the donor.
- Accept a series of immunizations for red blood cells administered under the supervision of our physician.
Yes. The red blood cells will be tested for infectious disease markers as required by the FDA.
- Red blood cell donors are qualified by a two year process of use in a limited number of donors.
- Cells used for immunization are at least one year old.
- The initial test results that were determined at the time of each donation will be confirmed by repeated tests performed on the donor one year later.
All equipment used to give the immunization is sterile, used only for you and disposed of after use.
Yes, whenever your antibody level drops, immunizations may be given.
Everyone’s immune system is different. Most donors who develop the antibody will do so in the first 12 months after the immunization. Once you develop the antibody, your plasma will be used to manufacture Rh immune globulin.
If you never develop the antibody, you can still donate as normal source plasma.
No. We are proud that some of our Anti-D donors have been with the program for over 15 years. Only in the highly unlikely occurrence of an incompatible blood transfusion, or an organ transplant would there be any risk
Yes, the requirements are as follows:
- Able to meet the requirements of being a source plasma donor
- If female, post-menopausal or surgically sterile
- Willing to make a commitment to the program and plan to remain in the geographic area to make the lengthy process worthwhile
- Not donating whole blood or plasma at any other facility while in the program
Women of childbearing age must provide documentation from a physician or have a medical record that states surgical sterility or post-menopausal state (in other words, without the ability to conceive and have children). Women past child-bearing age do not need any documentation.
The steps are simple:
- Undergo a screening medical evaluation by our physician to determine your eligibility for this program. This is at no cost to the donor.
- Accept a series of immunizations for red blood cells administered under the supervision of our physician.
Yes. The red blood cells will be tested for infectious disease markers as required by the FDA.
- Red blood cell donors are qualified by a two year process of use in a limited number of donors.
- Cells used for immunization are at least one year old.
- The initial test results that were determined at the time of each donation will be confirmed by repeated tests performed on the donor one year later.
All equipment used to give the immunization is sterile, used only for you and disposed of after use.
Yes, whenever your antibody level drops, immunizations may be given.
Everyone’s immune system is different. Most donors who develop the antibody will do so in the first 12 months after the immunization. Once you develop the antibody, your plasma will be used to manufacture Rh immune globulin.
If you never develop the antibody, you can still donate as normal source plasma.
No. We are proud that some of our Anti-D donors have been with the program for over 15 years. Only in the highly unlikely occurrence of an incompatible blood transfusion, or an organ transplant would there be any risk
Saving Lives is a
Major Commitment
We know you are ready to start this life-saving program, but please pause for a minute and realize that this program is a major commitment for your time. The program calls for donating twice per week, or at least 6 times per month. CSL Plasma will compensate you financially for your time.
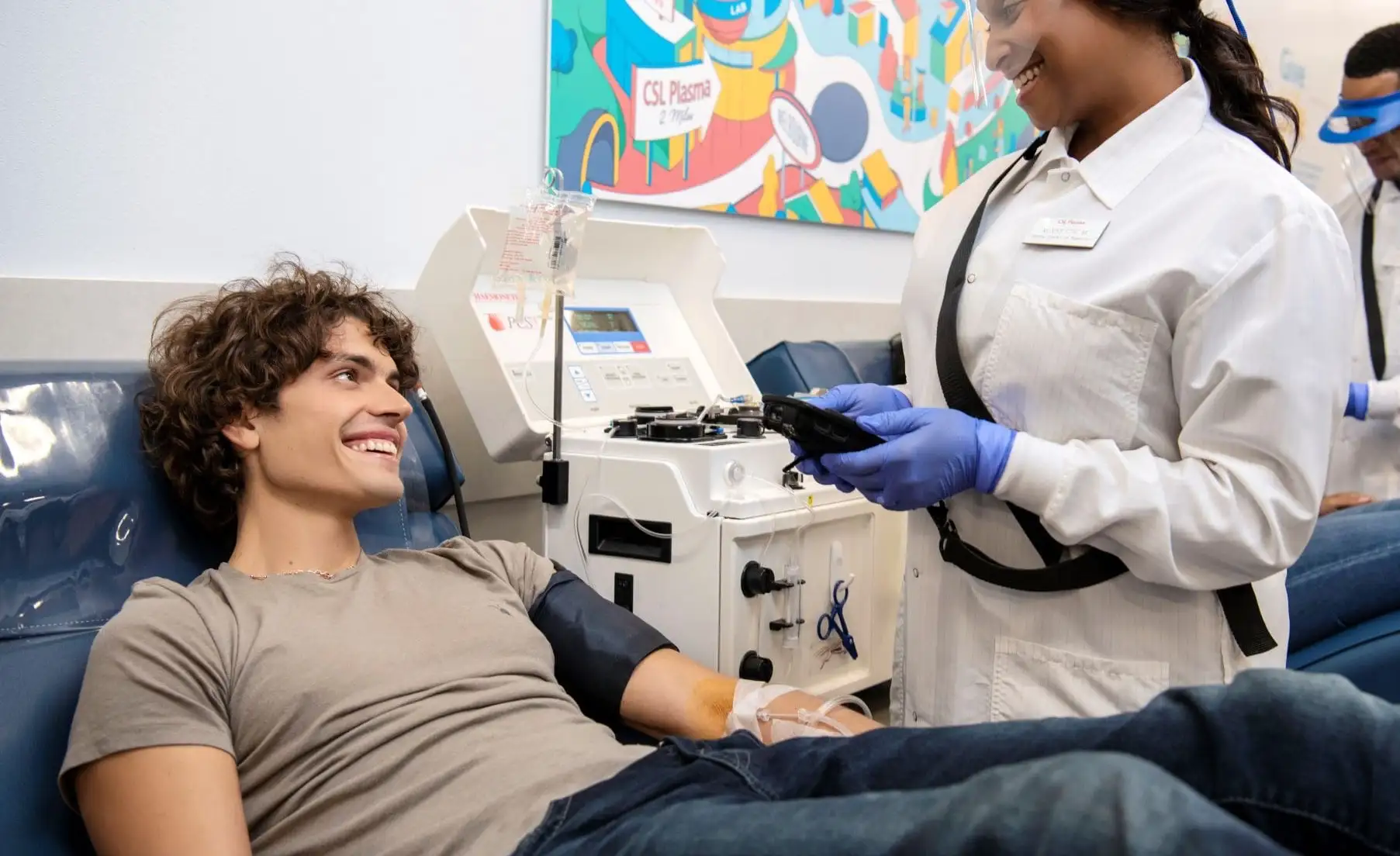
Your Life-Saving
Partner-CSL Plasma
CSL Plasma is committed to quality. Our staff receives the proper certification to operate this life-saving program. Our products and biomedical centers are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration, the Center for Biological Evaluation and Research, and also meet our own stringent quality standards. In addition, we operate one of the foremost testing laboratories in the world.


The result is an exceptional reputation in the healthcare industry. CSL Plasma is a global collector and supplier of plasma. We are proud of the lives that we save each and every day around the world. And we’re proud of you for helping us save lives.
